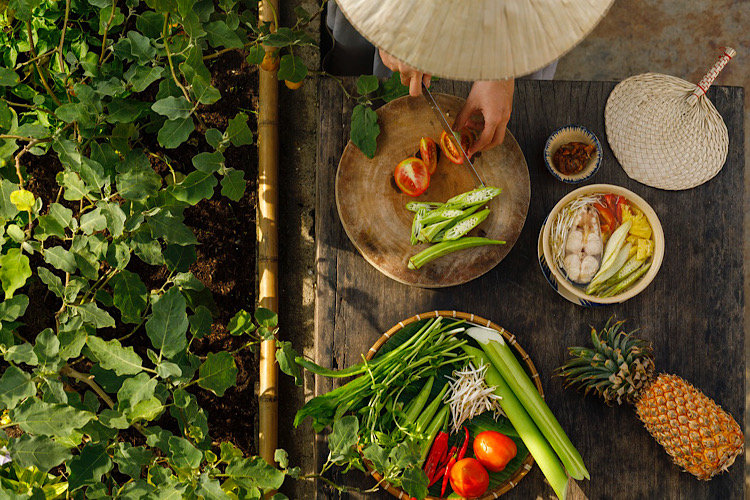
We’ve discovered delicious items that fit the WFPB diet, that is Whole Food Plant Based items, self-grown and not cumbered with chemical growth aids or genetic medication. Congratulations!
We’ll now explore how to prepare the WFPB as to reserve as much nutrients as possible.
As we’ve seen previously that original diet contains fresh and live foods, there was no indication of cooking involved. We read, “And God said, Behold, I have given you every herb bearing seed, which is upon the face of all the earth, and every tree, in the which is the fruit of a tree yielding seed; to you it shall be for meat.” (Genesis 1:29)
This is the foundational principle of food preparation, if it can be eat fresh and without processing, then that’s the ideal way to consume it. Plant foods contain live properties, oxygen, enzymes, vitamins, mineral, fluids and other important nutrients, such as carbs, protein and fats. We want all those good things as fresh as possible. Processing, even the mare severing the fruit off the tree branch will begin the the process of decay. The longer the time between harvest and consumption, or the further the food is from its whole form, the more sensitive nutrients are lost. It withers and is worth nothing, but to be burned.
This principle is clearly seen in here, “5 I am the vine, ye are the branches: He that abideth in me, and I in him, the same bringeth forth much fruit: for without me ye can do nothing. 6 If a man abide not in me, he is cast forth as a branch, and is withered; and men gather them, and cast them into the fire, and they are burned.”
Processing in our definition involves the activities which will change the foods from one form to another in the aim to make it perhaps more practical to cook, to eat or to preserve. Here are few besides cleaning:
- Chopping and slicing indicates using a knife to cut the food items in small piece, which sometimes is for practical purposes, but also for the reason of bringing out more of the flavor that is in the food.
- Blending and whisking is often used when finer processing is required, as when food items are used for sauces or stews.
- Pressing involves making the juice is the food item more available, sometimes for the purpose of entirely removing the pulp as in juicing, or pressed garlic, making some of the nutrients and flavors more available with less chewing required.
One of the reasons we process foods, is not because we always must do it, but the body requires a variation in how food is presented to the eye, nose and mouth, in order to better digest it. It contributes to the food being palatable, in other words more edible and enjoyed. “Unless the food is prepared in a wholesome, palatable manner, it cannot be converted into good blood, to build up the wasting tissues.” (Healthful Living 80.3)
This wouldn’t be anything knew, we find evidence that some foods required some processing.
“7 And the manna was as coriander seed, and the colour thereof as the colour of bdellium. 8 And the people went about, and gathered it, and ground it in mills, or beat it in a mortar, and baked it in pans, and made cakes of it: and the taste of it was as the taste of fresh oil.” (Numbers 11:7-8)
Having processed the food, we may be able to eat it in it’s:
- Raw condition is the ideal, however it’s not always expedient nor practical. Depending of the category of food, weather conditions, active or sedentary occupation etc, this will vary.
- Dehydrated condition is a method of drying out the food. It diminishes the liquids in the rod, but makes the nutrients more potent, makes its last longer and is a real treat when don’t it properly. This method is midway between raw and the rest of the methods, as temperatures normally don’t go above 40C.
- Baked condition is wonderful, beside for breads, quiches, pies, it’s greats for foods with a peal that require cooking. Foods are gently cooked and the leach of the nutrients is minimal compared too boiling, or so I’d like to think, on a simple basis that all liquids remain with the peal. Root veggies are good example of this foods. This method requires some patience.
- Boiled condition is where foods immersed in water. Some items require this much water not to dry out, in other cases where there’s limited time, root veggies instead of being baked, can be half boiled then tested in the oven for a crunchy texture. The water used to boiler is normally discarded.
- Stewed condition is the “baking” solution for boiling. Using minimal water, it’s incorporated into the food items that is been, stewed, this is slow cookery. The intention is to make the food flavor one with the water and herbs. In our home, we can simply not live without this.
- Fried condition is perhaps the method we should least and with caution. When use, it normally reach high temperatures, used with oil of some sort is used, both which can be a health hazardous, if not done skillfully and with appropriate products.
The take away is, while animal items that are used as food items, can cause worse illnesses; we should aim to eat our plant foods as whole and fresh as possible, lest we lose the nutritional values from them, making them less of a food.
Let us know, in the comments, how you prepare your food to be palatable, yet keeping its nutritional value up.